When it comes to protecting data and one way to ensure data availability, we use backup. A solid backup strategy will ensure that there is no single point of failure for your data, it will eliminate many risks It covers you if one copy of backup becomes corrupted or if you have been hit with unwanted disaster (hacker, ransomware, etc.).
3-2-1 backup rule
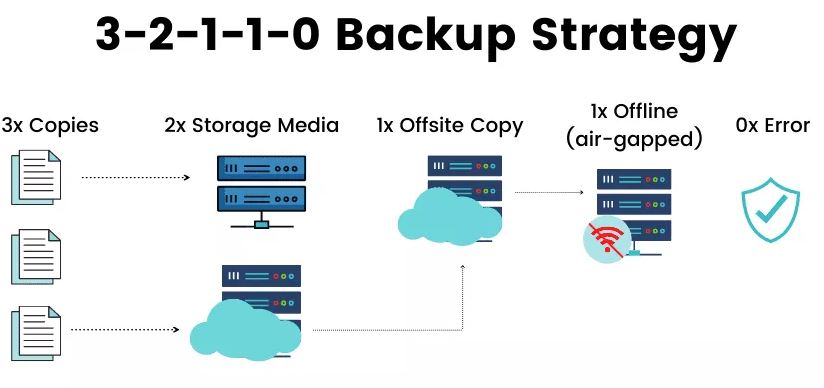
the 3-2-1 backup rule been around for decades and still many companies do follow the same rule. Due to raise of ransomware and other malicious threats they have extend the rule to 3-2-1-1-0.
principle of 3-2-1 are as follow:
• 3: The number of copies of data that you should have for all your backup jobs
• 2: The number of media types you should use for your backup
• 1: The number of data going offsite
And we the new extent:
• 1: The number of copies offline (air-gapped) or having immutability
• 0: Zero errors after media testing
RPO & RTO
Before we go deep into the mentioned rule, there are two terms which you should take in the account when you are going to build your backup strategy or data protection plan, which are Recovery Point Object (RPO) and Recovery Time Object (RTO):
RPO: simply means maximum amount of data that your organization can tolerate losing. This actually gets defined in your backup job schedule.
For example when you keep your backup schedule on daily basis at 1:00 PM, you are saying that you can lose up to one day of data when it comes to restoring it.
RTO: how many hours your business can be down without data. RTO is the amount of time it will take to restore your data and application to normal operations before the outage or data loss.
Now that we know what RPO, and TRO means lets get deep into our 3-2-1-1-0 rule:
3: Keeping at least 3 copies of your data
You should keep at least 3 copies of your data (your original data and 2 more copies as backup).each copy will bring a new cost to the business but having at least two copies will remove the single point of failure from your backup strategy as your backup solution usually seat in the same location as your original data (same DC) which could get affected with any disaster so the second backup often (hopefully) will be place somewhere far from the first backup
2: keep your backup on two different media
It is not recommended to keep your backup copies on the same media. it is recommended that each copy to use a different media. Usually, first copy goes to local storage (or SAN, NAS) and second copy goes to tape, external disk, cloud storage and etc.
1: number of copies of data going offsite
It is recommended that you keep a copy of your data in a physical location where the primary data and primary backup is located. The offsite cloud be your remote office, DR or cloud storages. You can even use Tape or external disk which needs to be stored in a separate secure physical location.
1: The number of copies offline (air-gapped) or having immutability
It is recommended that you keep one of your backups copied offline. That means there should be no connection to the backup so in case your environment gets compromised which all your online and connected devices and data can be impacted, you will have a copy which is offline.
It is also recommended to encrypt your offline copy for protection.
you can use rotating disk, tapes, object storages with immutability for this purpose.
0: Zero errors after media testing
finally and the most important part is to test your backup copies on recurring interval to ensure they are error free. You need to periodic restoration to confirm that you can actually restore the needed data application.